publications
2025
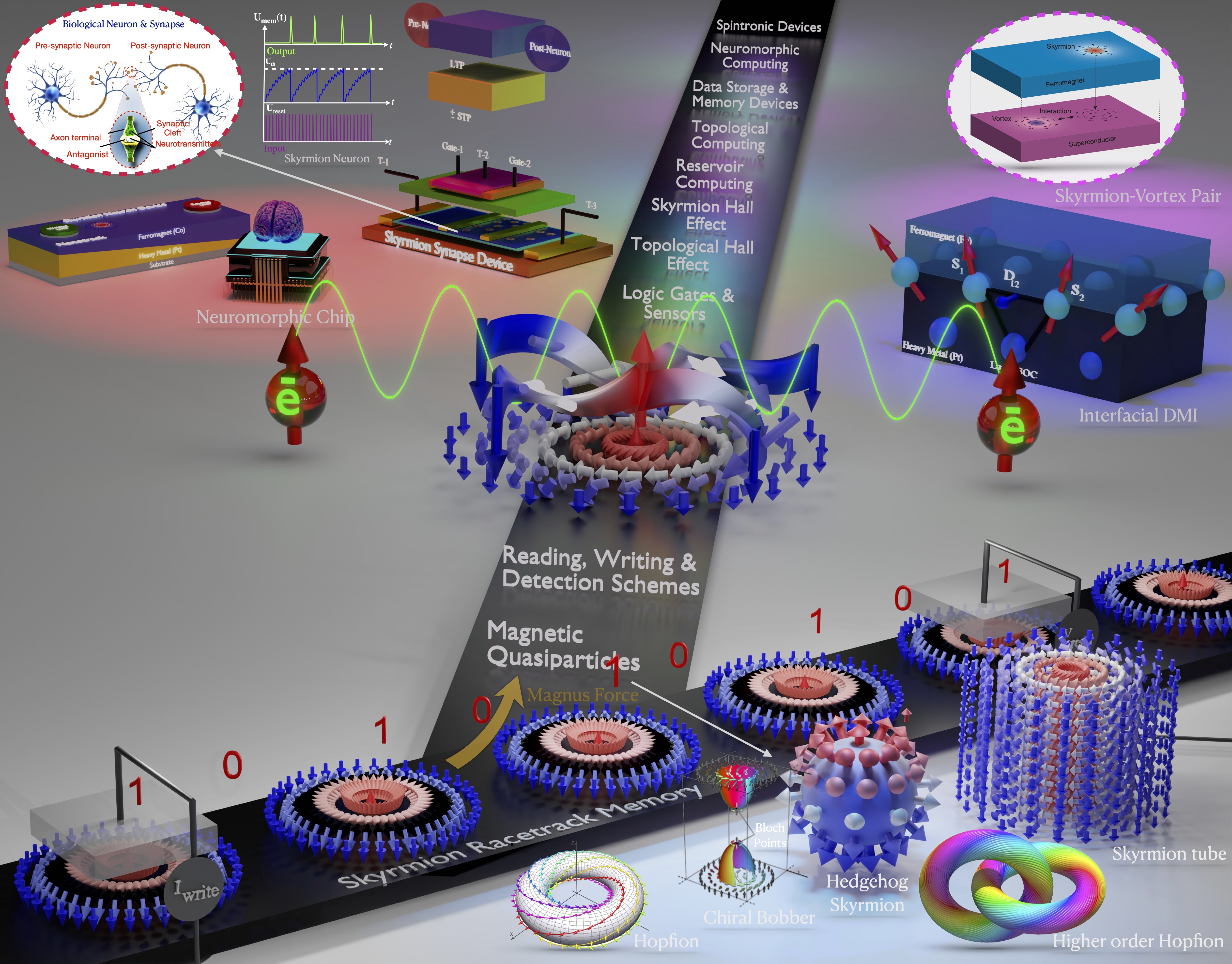
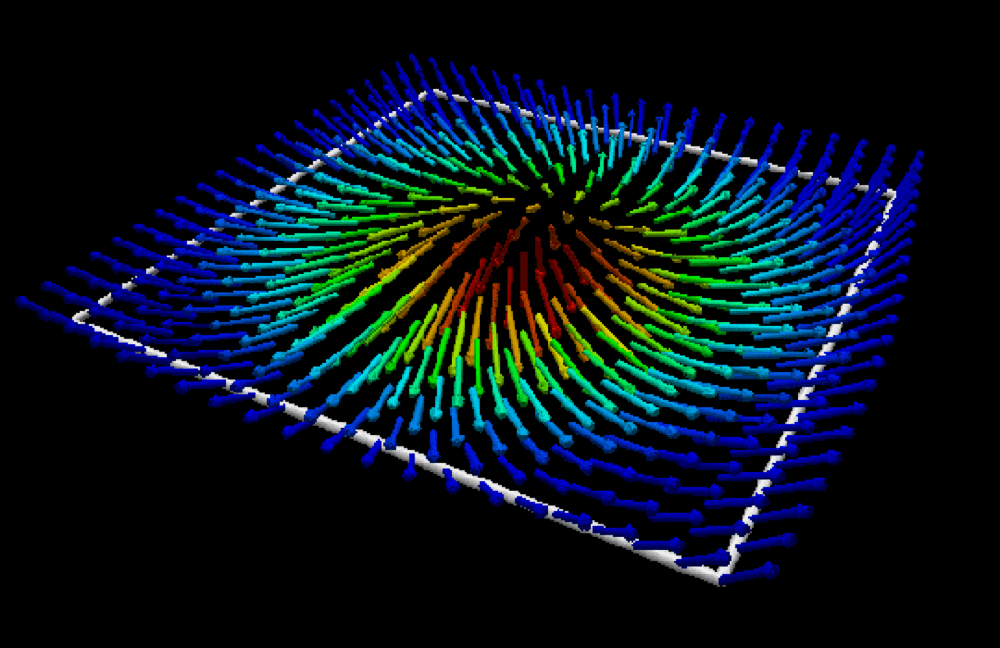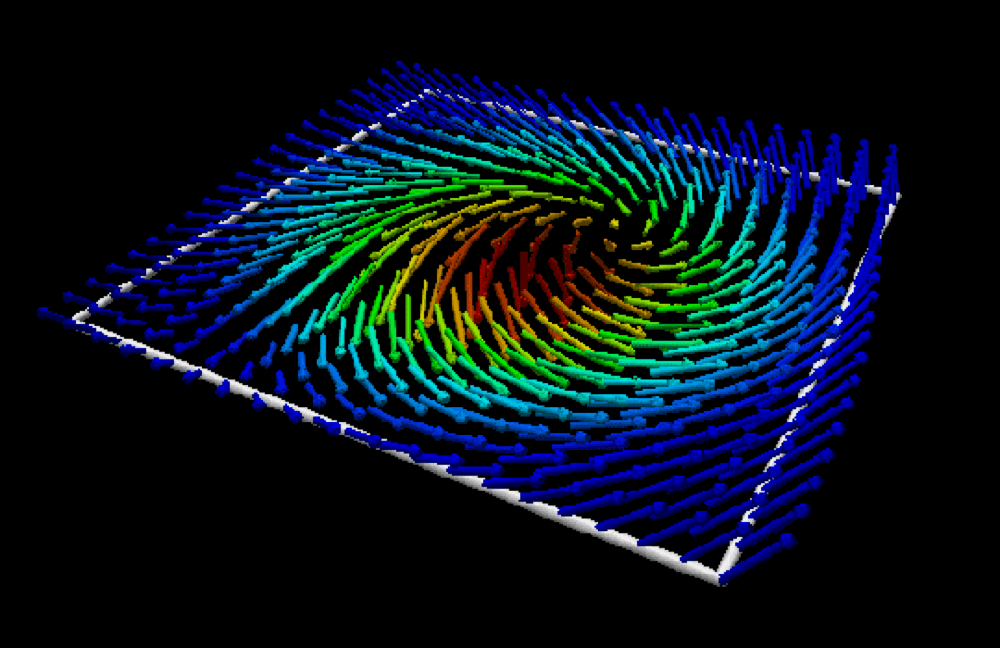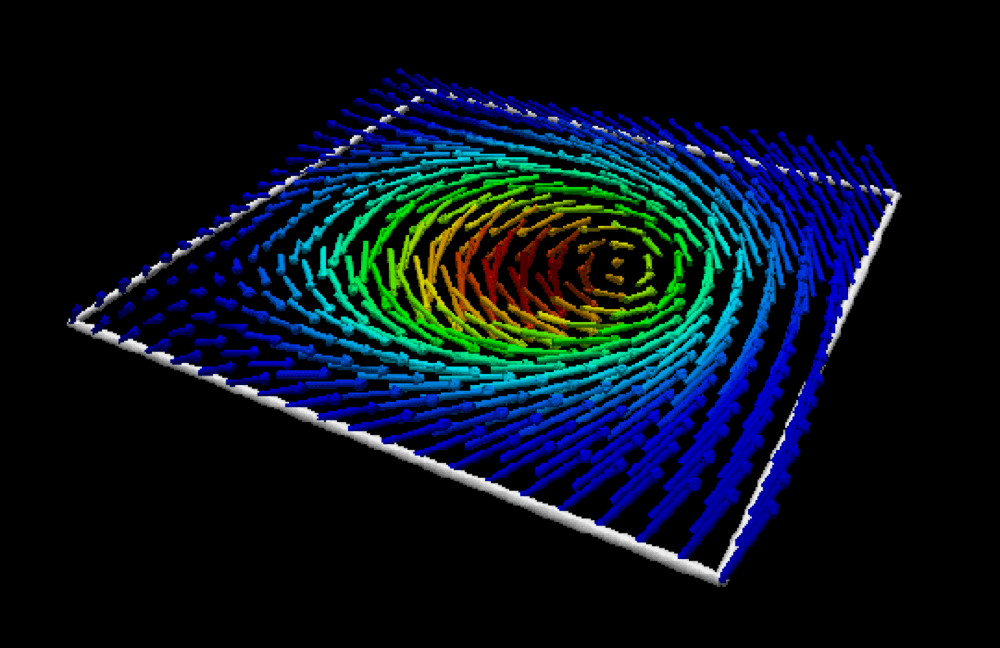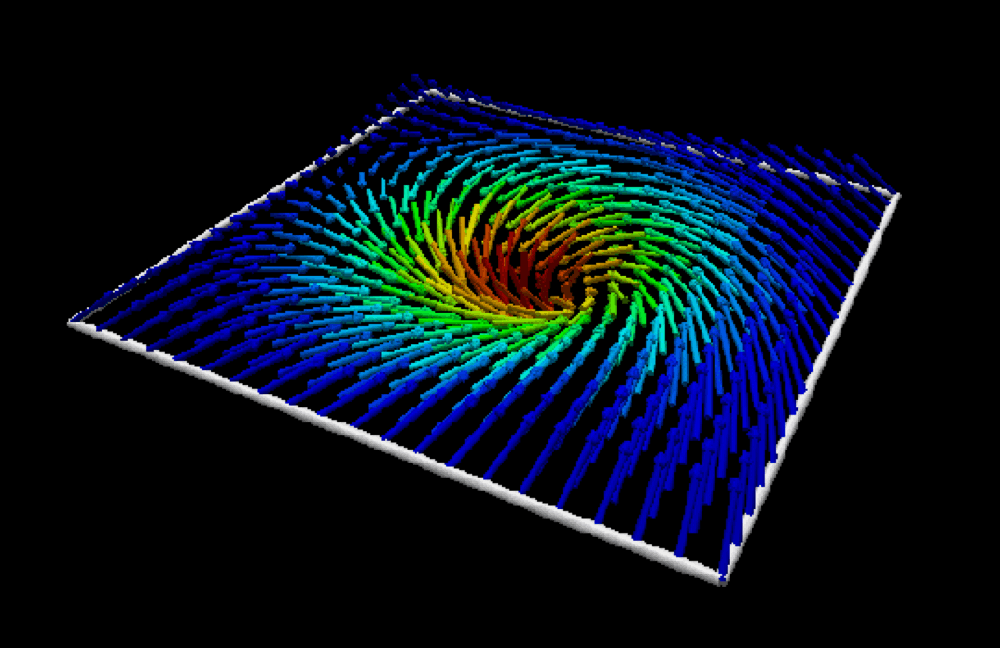
- Magnetic skyrmion: from fundamental physics to pioneering applicationsKishan Mishra, Aijaz H. Lone, Srikant Srinivasan, and 2 more authorsApplied Physics Reviews. More Information can be found here , Feb 2025
The article is featured on Applied Physics Review, AIP.
Skyrmionic devices exhibit energy-efficient and high-integration data storage and computing capabilities due to their small size, topological protection, and low drive current requirements. So, to realize these devices, an extensive study, from fundamental physics to practical applications, becomes essential. In this article, we present an exhaustive review of the advancements in understanding the fundamental physics behind magnetic skyrmions and the novel data storage and computing technologies based on them. We begin with an in-depth discussion of fundamental concepts such as topological protection, stability, statics, and dynamics essential for understanding skyrmions, henceforth the foundation of skyrmion technologies. For the realization of CMOS-compatible skyrmion functional devices, the writing and reading of the skyrmions are crucial. We discuss the developments in different writing schemes such as STT, SOT, and VCMA. The reading of skyrmions is predominantly achieved via two mechanisms: the magnetoresistive tunnel junction TMR effect and topological resistivity. So, a thorough investigation into the skyrmion Hall effect, topological properties, and emergent fields is also provided, concluding the discussion on skyrmion reading developments. Based on the writing and reading schemes, we discuss the applications of the skyrmions in conventional logic, unconventional logic, memory applications, and neuromorphic computing, including a model of a skyrmion-based SNN architecture achieving over 90% accuracy on MNIST and fashion-MNIST datasets. Furthermore, we outline the potential of skyrmion-hosting Majorana zero modes in emerging topological quantum computation and helicity-dependent skyrmion qubits.
@article{10.1063/5.0223004, author = {Mishra, Kishan and Lone, Aijaz H. and Srinivasan, Srikant and Fariborzi, Hossein and Setti, Gianluca}, title = {Magnetic skyrmion: from fundamental physics to pioneering applications}, journal = {Applied Physics Reviews}, volume = {12}, number = {1}, pages = {011315}, year = {2025}, month = feb, issn = {1931-9401}, doi = {10.1063/5.0223004}, url = {https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0223004}, eprint = {https://pubs.aip.org/aip/apr/article-pdf/doi/10.1063/5.0223004/20377552/011315\_1\_5.0223004.pdf}, dimensions = {true}, }
2024
- Magnetic soliton-based LIF neurons for spiking neural networks (SNNs) in multilayer spintronic devicesKishan MishraAIP Advances. More Information can be found here , Dec 2024
The article is featured on AIP Advances, AIP.
Neuromorphic computing, inspired by biological nervous systems, is gaining traction due to its advantages in latency, energy efficiency, and algorithmic complexity compared to traditional artificial neural networks. This has spurred research into artificial synapses and neurons that replicate brain functions. Spintronic-based technologies, particularly domain walls (DWs) and skyrmions (SKs), have shown remarkable potential for brain-inspired computing, facilitating energy-efficient data storage and advancing beyond CMOS computing architectures. Researchers have proposed various DWs- and Sks-based neuromorphic architectures for neurons and synapses. Leveraging magnetic multilayer structures, we propose a magnetic soliton that incorporates both DWs- and Sks-based magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ) device structures to emulate leaky integrate-and-fire (LIF) characteristics. These characteristics are controlled by spin–orbit torque (SOT)-driven motion within ferromagnetic thin films. By strategically placing the reading block and utilizing a combination of SOT and varying demagnetization energy, we achieve modified LIF neuron characteristics in both DW and Sks MTJ devices. The co-action of soliton dynamics across the nanotrack during the application of the current pulse, along with edge repulsion and variations in demagnetization energy, exploits LIF spiking behavior. Theoretical and micromagnetic analyses reveal that the transitory tunable positions of Sks and the total magnetization of the free layer for DWs mimic the membrane potential of biological neurons. Initial studies on multilayer DW-based LIF characteristics showed promise; however, maintaining leaky behavior required a constant negative current, which is energy inefficient. By incorporating the non-volatile properties of skyrmions and adding a chiral Dzyaloshinskii–Moriya interaction term, we further explored LIF dynamics, yielding encouraging results. Our proposed neuron model, implemented in fully connected and convolutional layers, achieves over 95% classification accuracy on the MNIST and Fashion MNIST datasets using a modified spike-based backpropagation method. With nanosecond latency, these spiking neuron devices, when integrated with CMOS, pave the way for high-density, energy-efficient neuromorphic computing hardware.
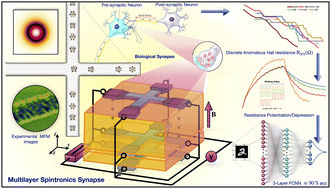
@article{10.1063/5.0232395, title = {Magnetic soliton-based LIF neurons for spiking neural networks (SNNs) in multilayer spintronic devices}, author = {Mishra, Kishan}, journal = {AIP Advances}, volume = {14}, number = {12}, year = {2024}, month = dec, issn = {2158-3226}, doi = {10.1063/5.0232395}, publisher = {AIP Publishing}, eprint = {https://pubs.aip.org/aip/adv/article-pdf/doi/10.1063/5.0232395/20304533/125119\_1\_5.0232395.pdf}, url = {https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0232395}, dimensions = {true}, } - Multilayer Ferromagnetic Spintronic Devices for Neuromorphic Computing ApplicationsAijaz H Lone, Xuecui Zou, Kishan Mishra, and 3 more authorsNanoscale, Dec 2024
@article{lone2024multilayer, title = {Multilayer Ferromagnetic Spintronic Devices for Neuromorphic Computing Applications}, author = {Lone, Aijaz H and Zou, Xuecui and Mishra, Kishan and Singaravelu, Venkatesh and Fariborzi, Hossein and Setti, Gianluca}, journal = {Nanoscale}, year = {2024}, doi = {10.1039/D4NR01003E}, url = {https://doi.org/10.1039/D4NR01003E}, dimensions = {true}, publisher = {Royal Society of Chemistry} }
2023
- Magnetic Skyrmion: From Fundamental Physics to Pioneering ApplicationsKishan Mishra, Aijaz H Lone, Srikant Srinivasan, and 2 more authorsarXiv preprint arXiv:2308.11811, Dec 2023
@article{mishra2023magnetic, title = {Magnetic Skyrmion: From Fundamental Physics to Pioneering Applications}, author = {Mishra, Kishan and Lone, Aijaz H and Srinivasan, Srikant and Fariborzi, Hossein and Setti, Gianluca}, journal = {arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.11811}, doi = {2308.11811}, dimensions = {true}, url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2308.11811}, year = {2023} }
2020
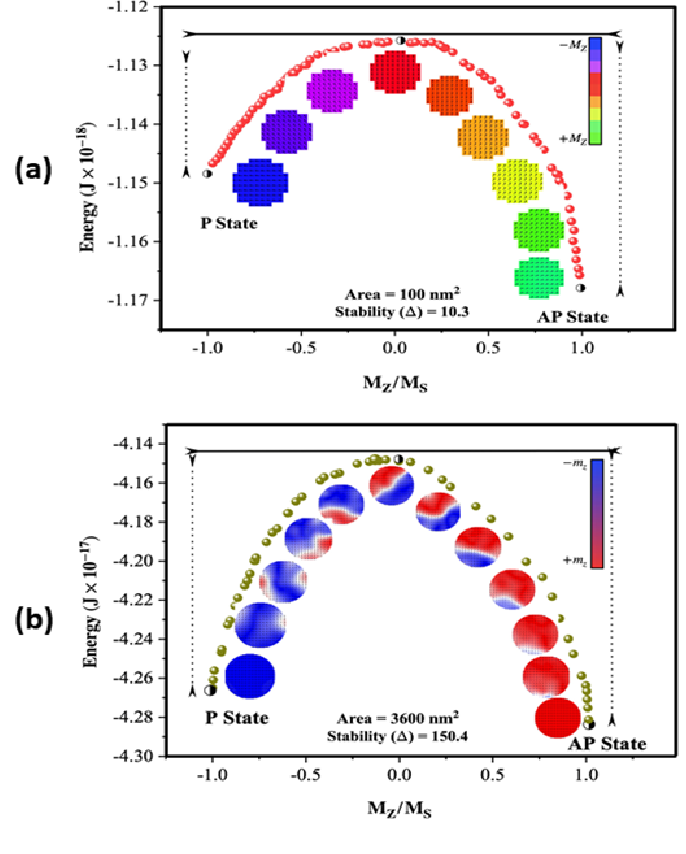
- Cross-sectional area dependence of tunnel magnetoresistance, thermal stability, and critical current density in MTJAijaz H Lone, Shivangi Shringi, Kishan Mishra, and 1 more authorIEEE Transactions on Magnetics, Dec 2020
@article{lone2020cross, title = {Cross-sectional area dependence of tunnel magnetoresistance, thermal stability, and critical current density in MTJ}, author = {Lone, Aijaz H and Shringi, Shivangi and Mishra, Kishan and Srinivasan, Srikant}, journal = {IEEE Transactions on Magnetics}, volume = {57}, number = {2}, pages = {1--10}, year = {2020}, doi = {10.1109/TMAG.2020.3039682}, dimensions = {true}, url = {https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/9265225/}, publisher = {IEEE} }